Electronic
Components
V=RA
This is one of the most important formulæ in
electronics. From it you can know what resistance to incorporate in
a circuit of a specific voltage to get a precise current. V
is the volatge (in Volts). R is the resistance (in Ohms). A
is the current (in Amperes). You can move the variables around to suit
your needs: R=V/A or A=V/R.
For example, if you want to know what resistance to put in a circuit
where the BS2 turns a LED on and off you can do the following:
- The BS2 outputs 5V.
- A LED usually drops the voltage by 1.7V
and requires 20mA of current to be at full brightness.
- So the total voltage in this circuit is 5V - 1.7V = 3.3V
- The needed current is 20mA = 0.02A
- Plug those values in the formulae R = V/A = 3.3/0.02 = 165
- Therefore you need a resistor of aproximately 165 Ohms in the
circuit.
BATTERY
A battery is a source of power. It has a specific voltage
and current.
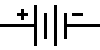 schematic representation of a battery
schematic representation of a battery
RESISTOR
A resistor limits the amount of current in a circuit.
It is electronic component you will probably use the most. Resistors
come in all different shapes and sizes. They dissipate heat as a result
of their opposing electricity, and are therefore rated both in terms
of their resistance (how much they oppose the flow of electrons) and
their power capacity (how much power they can dissipate before becoming
damaged).
 shematic representation of a resistor
shematic representation of a resistor
The resistance is calculated with the color code on
the resistor. Danny Goodman made
a nifty resistance value calculator:
POTENTIOMETER
A potentiometer is a resistor with a variable resistance.
They have various forms. You will often see them as knobs or sliders.
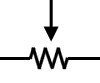 shematic representation of a potentiometer
shematic representation of a potentiometer
They usually have 3 pins. The pin in the middle is the positive pin.
The 2 other pins are ground (GND) pins.
Many things can serve as potentiometers. Your skin,
liquid substances, metallic materials that can be deformed, etc. can
all act like potentiometers.
CAPACITOR
You can imagine a capacitor as a tank that can be charged
and discharged. A capacitor stores voltage as electrical energy. When
a DC current is applied across a capacitor, positive charge builds on
one plate (or set of plates) and negative charge builds on the other.
The charge will remain until the capacitor is discharged.
Capacitors can be polar or not. Polar capacitors have a positive side
and a negative side. Usually the longest pin of a polar capacitor is
the positive side.
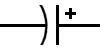 shematic representation of a polar capacitor
shematic representation of a polar capacitor
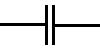 non-polar capacitor
non-polar capacitor
The strength of a capacitor is called capacitance and is measured in
farads (F).
DIODE
Diodes are one way components. They are polar. They
allow you to make sure the current flows in one specific way of the
circuit. Again, in general, the longest pin of a diode is the positive
side.
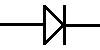 shematic representation of a diode
shematic representation of a diode
LIGHT-EMITTING DIODE
A variant of the common diode is the light-emitting
diode or LED.
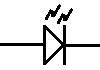 shematic representation of a LED
shematic representation of a LED
There are many types of LEDs on the market. LEDs have various properties:
-
Voltage Drop (V): the voltage drawn by the LED.
-
Current (mA): the maximum current you can give it
for optimal brightness.
-
Brightness (mCd): the brightness of a LED is measured
in millicandellas. 1 candella (Cd) is equivalent to the brightness
of 1 candle.
-
Color (nm): the color is measured as a wavelength
in nanometers. In general, LEDs are also labeled with the corresponding
color.
|
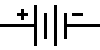 schematic representation of a battery
schematic representation of a battery shematic representation of a resistor
shematic representation of a resistor shematic representation of a potentiometer
shematic representation of a potentiometer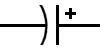 shematic representation of a polar capacitor
shematic representation of a polar capacitor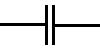 non-polar capacitor
non-polar capacitor 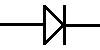 shematic representation of a diode
shematic representation of a diode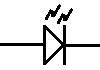 shematic representation of a LED
shematic representation of a LED